Difference between Addition Polymerization and Condensation Polymerization?
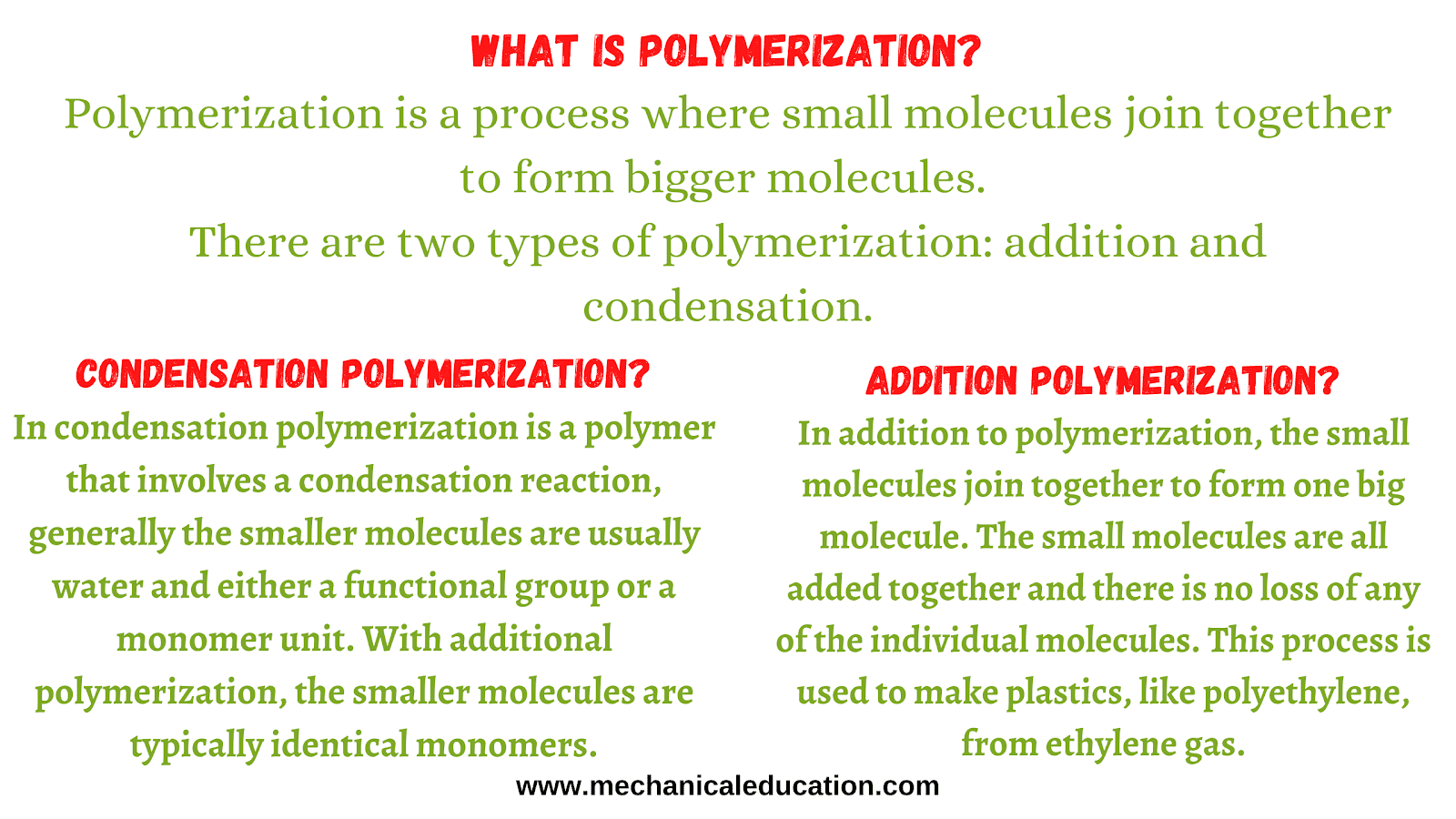
What is Polymerization?
Polymerization is a process where small molecules join together to form bigger molecules. There are two types of polymerization: addition and condensation.
Polymerization is a chemical process that yields chains of repetitive units called polymers. This process is used to create an entirely new product by linking together molecules of two different products. The two products are called monomers and the resulting polymer belongs to one of three types: addition polymerization, condensation polymerization, or ring-opening polymerization.
In general, there are two types of polymerization reactions: addition and condensation. In an additional reaction, two small molecules join together to form one larger molecule. In a condensation reaction, one molecule splits into two smaller molecules.
What is Condensation Polymerization?
In condensation polymerization is a polymer that involves a condensation reaction, generally the smaller molecules are usually water and either a functional group or a monomer unit. With additional polymerization, the smaller molecules are typically identical monomers.
CONDENSATION POLYMERIZATION is where one molecule reacts with itself by adding four gaseous chemical groups called free radicals
What is Addition Polymerization?
In addition to polymerization, the small molecules join together to form one big molecule. The small molecules are all added together and there is no loss of any of the individual molecules. This process is used to make plastics, like polyethylene, from ethylene gas.
ADDITION POLYMERIZATION is an atom-by-atom reaction, where two unactivated monomers react to form a polymer. Monomers may be the same or they may be different. In addition, polymers form 3D structures by themselves, they do not need another agent to provide this. Thus it is generally used in materials science and engineering when the properties in the 2D plane of material are undesired for application in architecture or engineering. Examples include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PPS (Polyphenylsulfide).
Difference between Addition Polymerization and Condensation Polymerization Reaction:
In a condensation polymerization reaction, two molecules join together to form a larger molecule, and water is released as a by-product. This is the type of reaction that occurs when nylon is made from caprolactam and hexamethylenediamine.
In an addition polymerization reaction, monomers are added together to form a polymer chain. This is the type of reaction that occurs when polyethylene is made from ethylene gas.
Condensation Polymerizations are the opposite due to its mechanism. In addition, Polymerizations are easier to “track”. When the monomers combine they make -OH bonds leaving behind single H’s! When reading Condensation Polymoners you have (-OH) bonded (+H).
In condensation polymerization, two molecules join together to form a larger molecule, and water is released as a by-product. In addition to polymerization, two or more monomers join together to form a bigger molecule, and no water is released as a by-product.
One way to think about it is that in condensation polymerization, the water molecule is “consumed” in the process of forming the larger molecule. Whereas in addition to polymerization, the water molecule is not used up, it’s just not released as a by-product.